What is steroid?
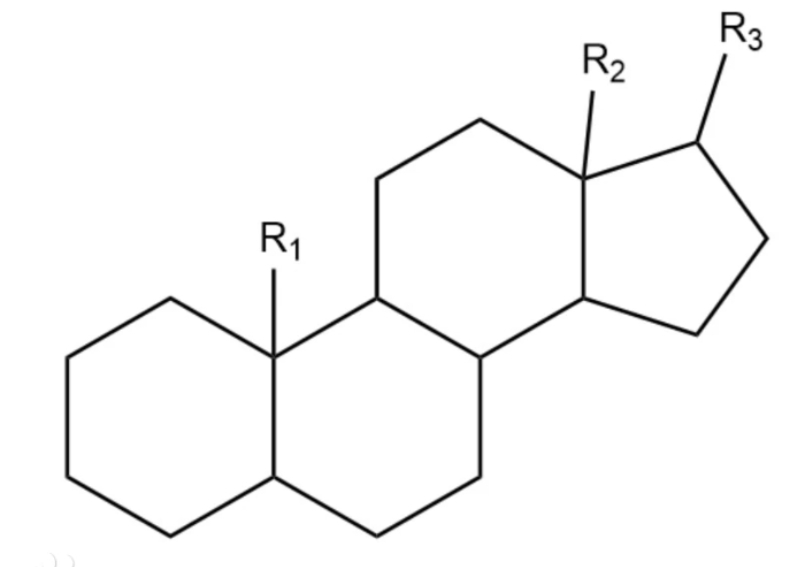
Steroids are natural or synthetic organic compounds with a molecular structure of 17 carbon atoms arranged in four rings. They include sex hormones, adrenal cortical hormones, bile acids, and sterols.
steroid, any of a class of natural or synthetic organic compounds characterized by a molecular structure of 17 carbon atoms arranged in four rings. Steroids are important in biology, chemistry, and medicine.
1. Steroid hormones are endogenous substances found in the study of mammalian endocrine systems.
2, between 1932 and 1939, obtained pure crystal of Estrone (1932), Estradiol (1932), Testosterone (1935) and Corticosterone (1939) from the gland, Then the chemical structure of steroid was elucidated, and a new field of steroid chemistry and steroid drug chemistry was created. Many significant achievements followed.
3. Invented the semi-synthetic production of steroid drugs with Diosgenin as raw material, which expanded the production scale and reduced the cost.
4, the discovery of adrenocortical hormone in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and its important value in immune regulation, so that steroid drugs become indispensable drugs in the hospital.
5. The success of the study of steroid oral contraceptives has brought human birth control to a new level.
The steroid group includes all the sex hormones, adrenal cortical hormones, bile acids, and sterols of vertebrates, as well as the molting hormones of insects and many other physiologically active substances of animals and plants. Among the synthetic steroids of therapeutic value are a large number of anti-inflammatory agents, anabolic (growth-stimulating) agents, and oral contraceptives.
Different categories of steroids are frequently distinguished from each other by names that relate to their biological source—e.g., phytosterols (found in plants), adrenal steroids, and bile acids—or to some important physiological function—e.g., progesterones (promoting gestation), androgens (favouring development of masculine characteristics), and cardiotonic steroids (facilitating proper heart function).
Steroids vary from one another in the nature of attached groups, the position of the groups, and the configuration of the steroid nucleus (or gonane). Small modifications in the molecular structures of steroids can produce remarkable differences in their biological activities.
This article covers the history, chemistry, biological significance, and basic pharmacology of steroids. For more information about the physiological relevance and the pharmacological applications of steroids, see human endocrine system, endocrine system, and drug.
Thank you for your reading!
More popular steroid powder recommend: https://www.steroidsmedical.com/product-category/
 Domestic Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Domestic Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.