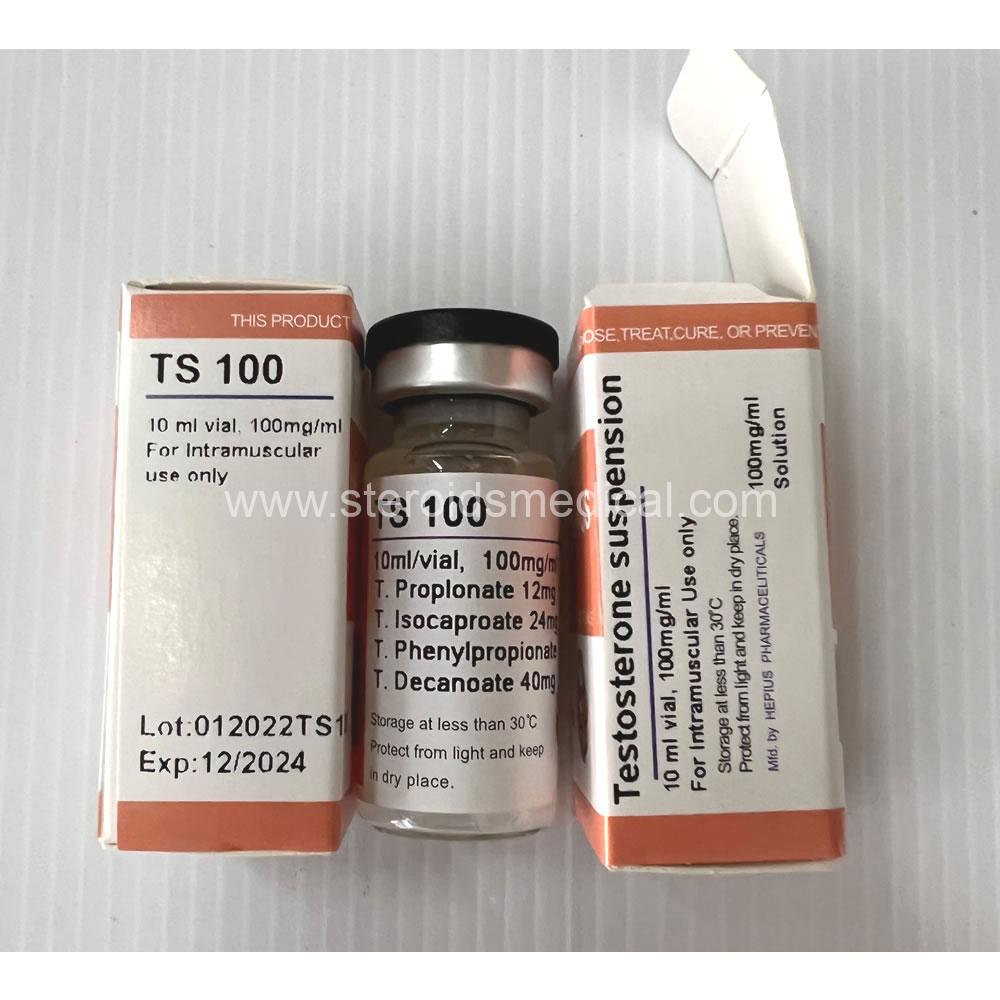
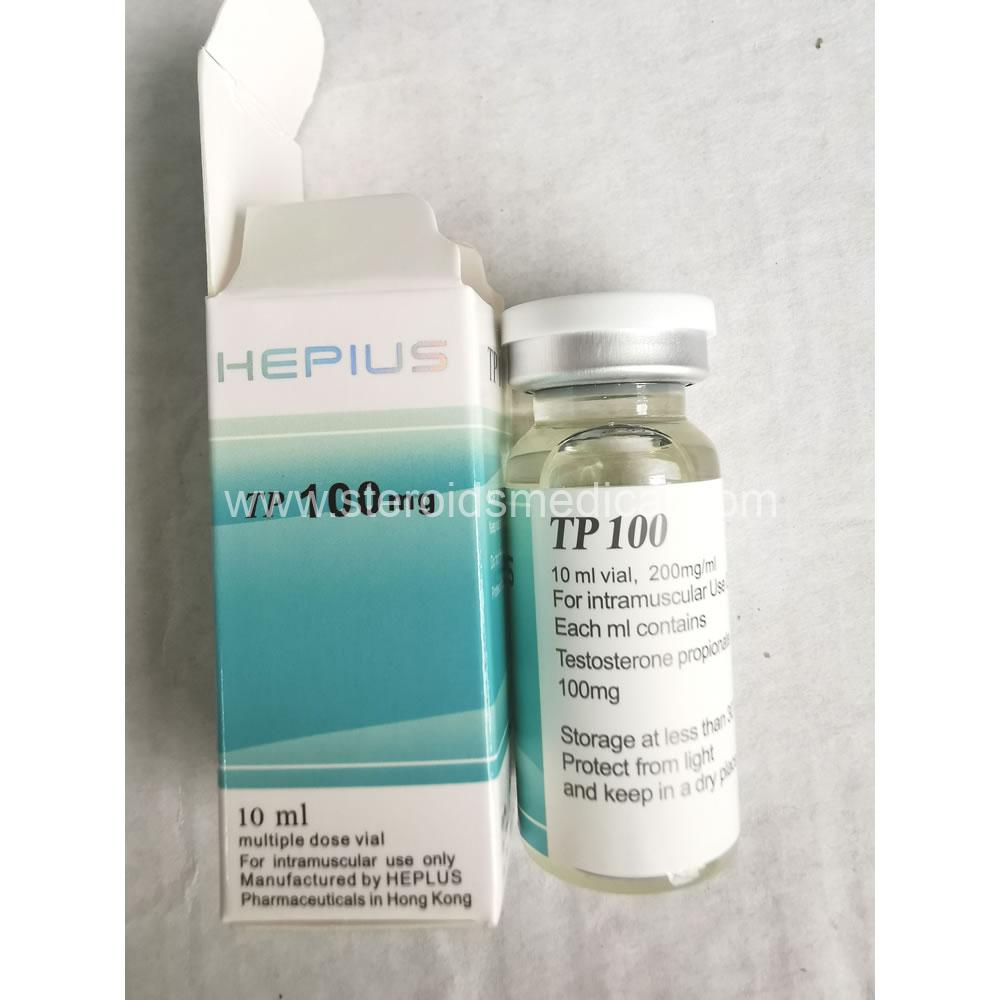
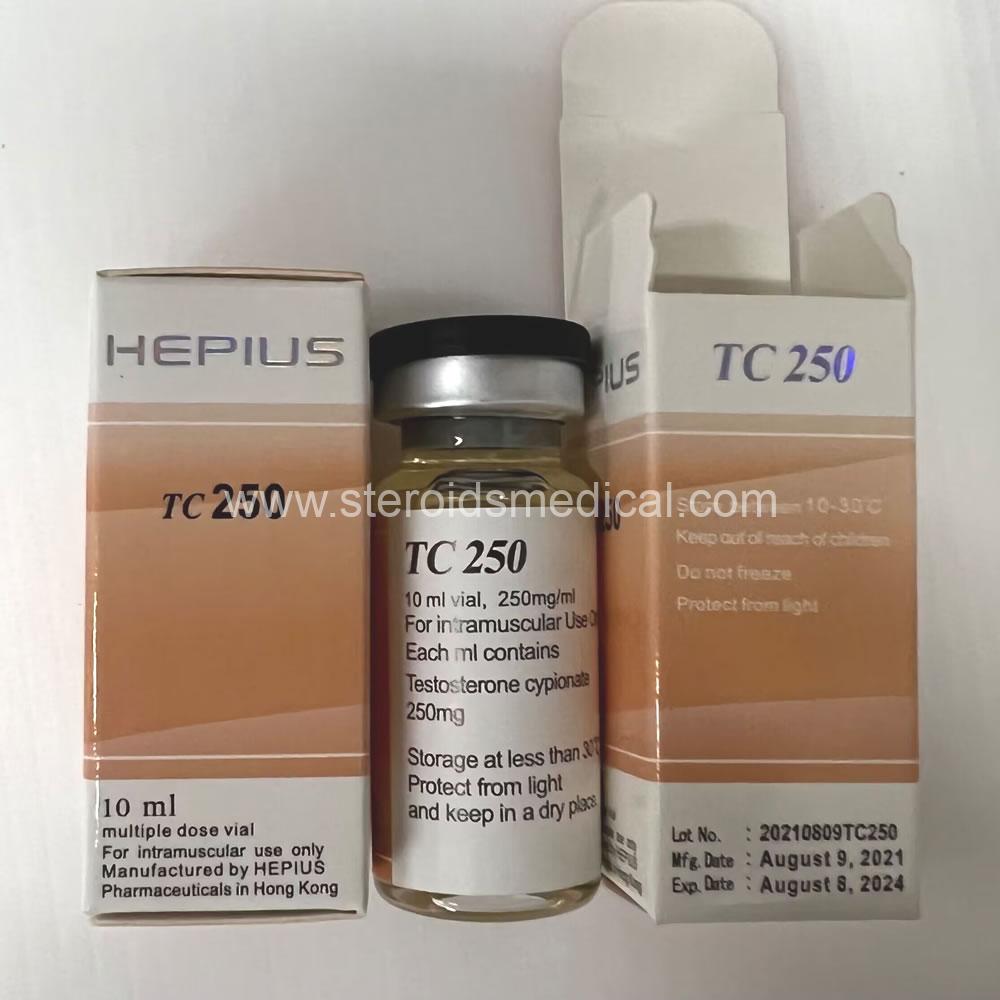
Testosterone undecanoate is an alternative form of testosterone that differs from testosterone enanthate primarily in its ester length and method of administration. Here’s a detailed description of testosterone undecanoate 300mg:
Chemical Structure: Testosterone undecanoate is an esterified derivative of testosterone. Unlike shorter esters like enanthate or propionate, undecanoate has a much longer ester chain (11 carbons), which slows down its release into the bloodstream after injection.
Administration: Unlike other injectable forms of testosterone that are typically administered every 1-2 weeks, testosterone undecanoate is unique in that it is formulated for intramuscular injection and is also available in an oral capsule form (though the 300mg is typically administered via intramuscular injections).
Pharmacokinetics: Testosterone undecanoate is characterized by its long-acting nature, providing sustained levels of testosterone in the bloodstream over an extended period. After intramuscular injection, testosterone undecanoate undergoes gradual release from the injection site into the bloodstream.
Medical Uses: It is primarily used in the treatment of hypogonadism in men, where the body does not produce enough testosterone. Testosterone undecanoate helps to restore testosterone levels to normal, alleviating symptoms such as low libido, fatigue, and loss of muscle mass and bone density.
Dosage: The typical dosage of testosterone undecanoate 300mg involves administration at intervals that can span several weeks. Specific dosing schedules should be determined by a healthcare provider based on individual patient response and needs.
Side Effects: Common side effects of testosterone undecanoate include acne, oily skin, increased body hair growth, and fluid retention. It may also affect cholesterol levels and can exacerbate certain conditions like sleep apnea. As with other forms of testosterone replacement therapy, there is a potential risk of cardiovascular issues with long-term use.
Monitoring: Patients using testosterone undecanoate should undergo regular monitoring of testosterone levels and potential side effects. Blood tests are typically conducted to ensure that testosterone levels remain within the therapeutic range and to monitor any adverse effects.
Safety Considerations: Testosterone undecanoate should not be used by individuals with prostate cancer or breast cancer (in men), severe cardiac, hepatic, or renal insufficiency, unless closely monitored by a healthcare provider. It is also important to avoid misuse or overuse of testosterone undecanoate, as it can lead to serious health complications.
Legal Considerations: Like other forms of testosterone replacement therapy, testosterone undecanoate is a controlled substance in many countries due to its potential for abuse and misuse. It is classified differently in various jurisdictions, so it’s important to adhere to local regulations.
Special Populations: Testosterone undecanoate may also be used in transgender hormone therapy, specifically for masculinization, under medical supervision and with appropriate monitoring.
How to Use It?
Using testosterone undecanoate 300mg involves a specific process to ensure safe and effective administration. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how it is typically used:
Preparation:
Consultation with a Healthcare Provider: Before starting testosterone undecanoate, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider, such as an endocrinologist or urologist, who specializes in hormone therapy. They will assess your medical history, perform necessary tests (including blood tests for hormone levels), and provide guidance on dosage and administration.
Prescription: Testosterone undecanoate is a prescription medication. Your healthcare provider will prescribe the appropriate dosage and frequency of administration based on your individual needs and health status.
Supplies: Gather all necessary supplies, including the testosterone undecanoate 300mg ampoules or vials, syringes (typically 1-3 mL), needles, alcohol swabs for sterilization, and a puncture-proof container for safe disposal of needles and syringes.
Administration (Intramuscular Injection):
Sterilization: Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water. Clean the rubber stopper of the vial with an alcohol swab to ensure sterility.
Drawing the Solution:
- Attach a new, sterile needle to the syringe.
- Draw air into the syringe equal to the amount of testosterone undecanoate you need to withdraw.
- Insert the needle into the vial and inject the air to equalize the pressure.
- Invert the vial and slowly draw the entire contents of the ampoule or vial into the syringe. Tap the syringe to remove air bubbles and ensure accurate measurement.
Injection Site:
- Choose a clean and sterile injection site, typically the gluteal muscle (upper outer quadrant) or the ventrogluteal muscle.
- Clean the injection site with an alcohol swab and allow it to dry.
Injection Technique:
- Hold the syringe like a dart at a 90-degree angle to the skin.
- Insert the needle quickly and smoothly into the muscle.
- Slowly push the plunger to inject the medication.
- Once injected, withdraw the needle swiftly and apply pressure to the injection site with a sterile cotton ball or gauze.
Disposal: Discard the used syringe and needle in a puncture-proof container according to local regulations.
Aftercare:
Monitoring: After administration, monitor for any immediate adverse reactions, such as swelling, pain, or redness at the injection site.
Follow-up: Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions regarding subsequent doses and any necessary blood tests to monitor hormone levels and overall health.
Adherence: Adhere strictly to the prescribed dosage schedule and do not adjust or stop treatment without consulting your healthcare provider.
Storage: Store testosterone undecanoate as per the manufacturer’s instructions, typically at room temperature away from light and moisture.
Additional Considerations:
- Rotate Injection Sites: Alternate injection sites (e.g., left and right gluteal muscles) to minimize tissue damage and discomfort.
- Health Monitoring: Regularly monitor your health, including cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and prostate health, especially with long-term use.
- Side Effects: Report any unusual symptoms or side effects to your healthcare provider promptly.
 Domestic Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Domestic Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.