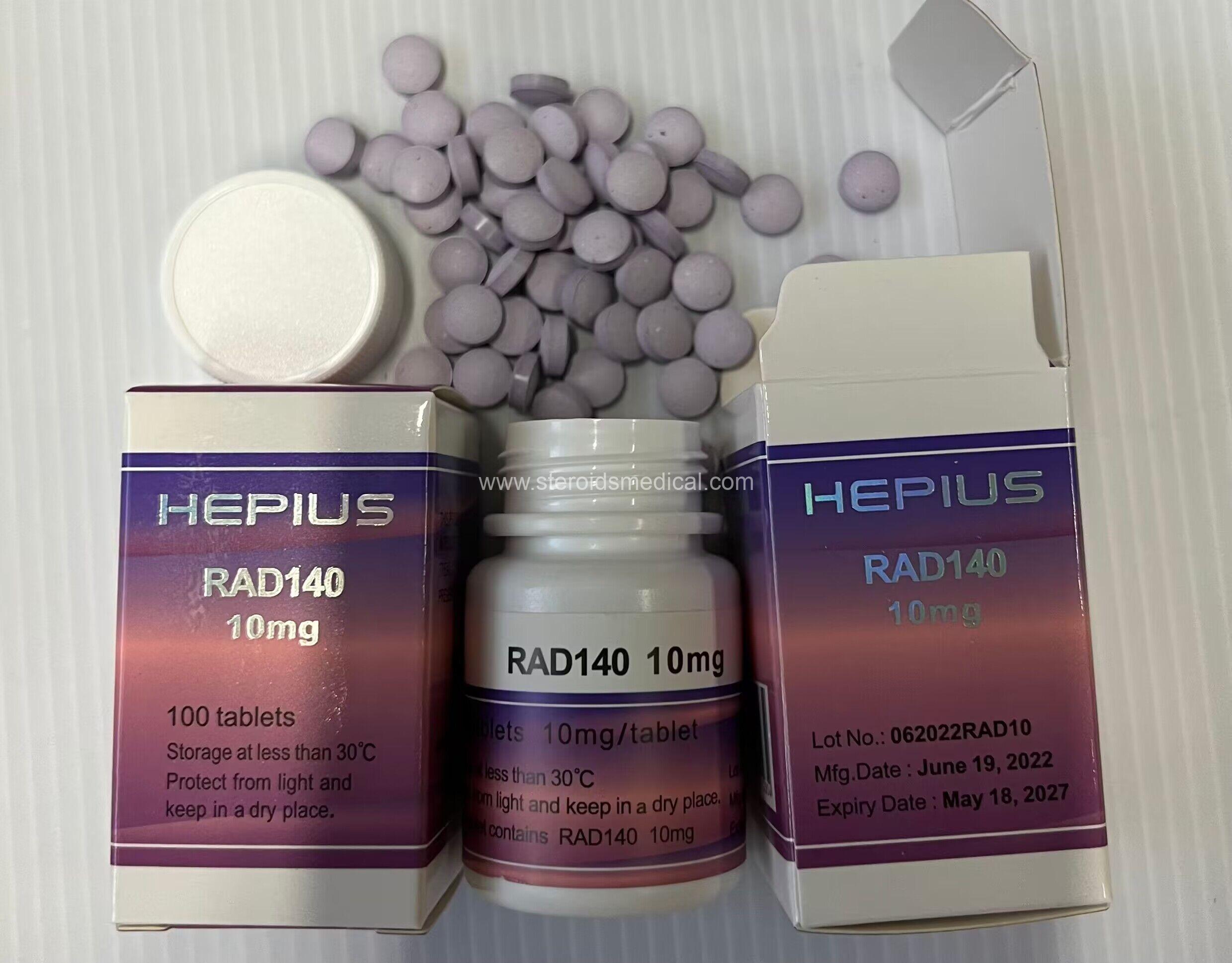
Description:
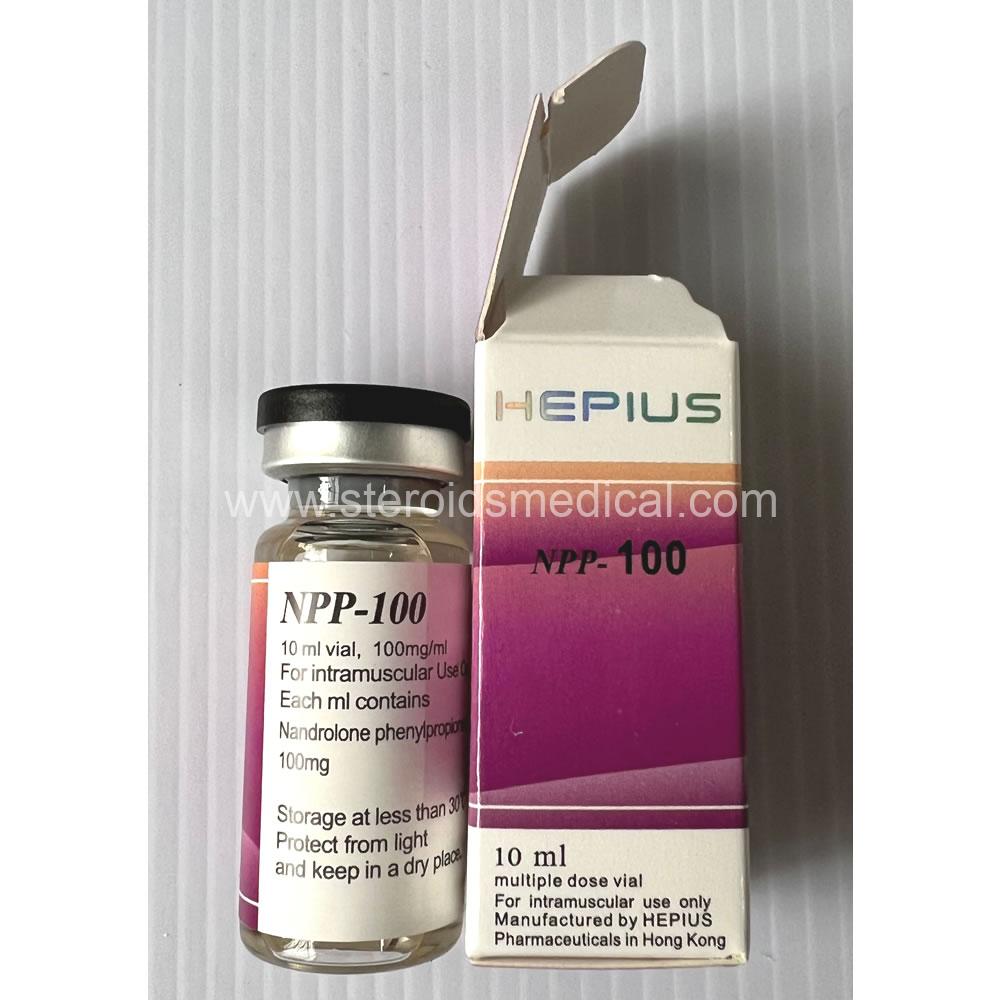
Nandrolone PhenylPropionate (NPP) is an anabolic steroid used to enhance muscle growth, strength, and recovery. It is a modified form of the hormone nandrolone, which has a shorter ester (phenylpropionate) attached, resulting in a faster release into the bloodstream compared to other nandrolone esters like Decanoate.
Key Points about NPP 100mg:
Dosage and Administration:
- Typically administered via intramuscular injection.
- Dosage can vary depending on the individual’s goals, experience, and tolerance. Common dosages range from 100mg to 600mg per week, often divided into multiple injections.
Benefits:
- Muscle Growth: Promotes lean muscle mass gains.
- Recovery: Enhances recovery by increasing protein synthesis and nitrogen retention.
- Joint Health: Often noted for its positive effects on joint health and pain reduction.
Side Effects:
- Estrogenic Effects: May cause water retention and gynecomastia (breast tissue growth in men) due to its conversion to estrogen. Anti-estrogens or aromatase inhibitors might be needed.
- Androgenic Effects: Possible hair loss, acne, and increased body hair growth.
- Cardiovascular Issues: Can negatively impact cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of heart disease.
- Suppression of Natural Testosterone: Can lead to decreased natural testosterone production, necessitating post-cycle therapy (PCT).
Cycle Duration:
- Typically used in cycles ranging from 8 to 12 weeks.
- Often stacked with other anabolic steroids like testosterone to maximize benefits.
Legal Status:
- Classified as a controlled substance in many countries, including the United States, where its use without a prescription is illegal.
Medical Use:
- Sometimes prescribed for medical conditions such as anemia and muscle-wasting diseases under strict medical supervision.
Precautions:
- Regular monitoring by a healthcare professional is recommended to manage potential side effects.
- Blood work should be done to check liver function, cholesterol levels, and hormone levels.
- Not recommended for use by women due to a high risk of virilization (development of male characteristics).
 Domestic Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Domestic Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.